Medical Education: Professional Educator
Medical Education 5: Faculty Development 1
516 - Designing the resident oncology rotation experience to match post-residency plans
Publication Number: 516.227
- SC
Stacy Cooper, MD (she/her/hers)
Assistant Professor
Johns Hopkins University
BALTIMORE, Maryland, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
ACGME requires that residents participate in at least 9 subspecialty rotations during training. Trainee engagement during each rotation may be a challenge as the goals of the rotation may not be aligned with those of the resident.
Objective:
To improve engagement of residents rotating through the 4-week pediatric oncology inpatient rotation, we designed and then evaluated an independent learning, case-based activity based on the resident’s future career goals.
Design/Methods:
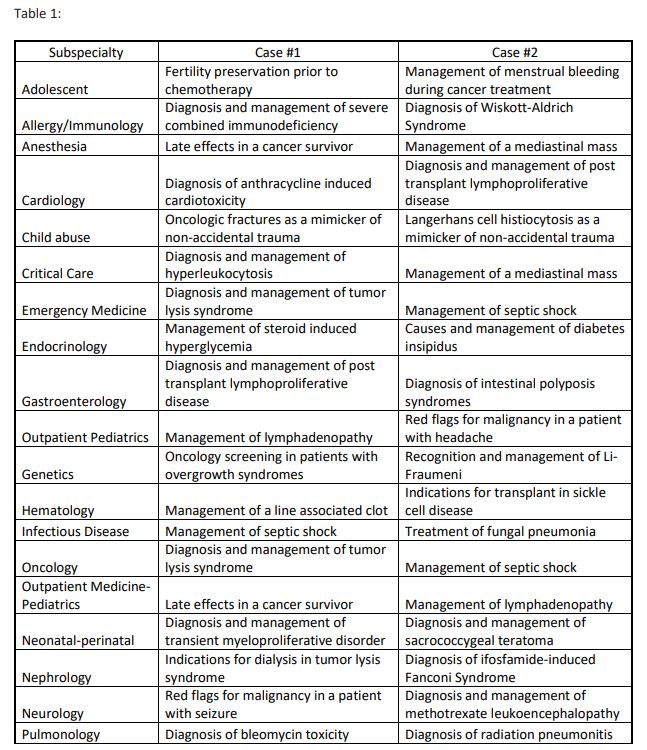
Through a modified Delphi process, p</span>ediatric faculty at a tertiary academic center were first asked to identify the most important oncology topics encountered in their practice. Within each discipline, the list was collated, and faculty were then asked to choose the two “highest yield” topics. This process was repeated until consensus was reached. Two cases for each post-residency career were then created that included interactive slides and a reading list. Beginning in July 2020, each resident identified their most likely career path after residency, and cases for that path were provided. At the end of the rotation, residents were surveyed asking how well the rotation prepared them for their career goals and their overall rating of the rotation (1=poor, 5=excellent). Data were compared with a similar survey of residents rotating July 2018- June 2020 (controls). Sixty-one percent (124/203) of faculty participated in identifying the topics (Table 1). From July 2020- June 2021, 30 residents having 13 different career goals rotated through oncology and all completed both cases. Of these, 25 (83%) responded to the survey compared with 28/32 response rate (88%) for the controls. In controls, 42% (13/32) felt that the rotation prepared them for their future career goals “very well” or “extremely well” compared with 68% (20/32) of those receiving the cases. Overall, 93% (28/30) of residents receiving the cases found them “very useful” or “extremely useful” with 12 indicating that they would like this activity expanded to other rotations. Overall rotation evaluations increased from a mean of 4.06 to 4.41 after the cases were added. Incorporation of a case-based learning activity tailored to the resident’s future career goals was perceived as useful by residents, increased their engagement and satisfaction in the rotation. Further study is needed to determine if this activity increased trainee knowledge.
Results:
Conclusion(s):