Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 1
221 - Risk stratify the hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus by the clinical and genetic factors
Publication Number: 221.329
- YC
Yuxi Chen
NA
Center for Molecular Medicine, Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, National Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai, China
Shanghai, Shanghai, China (People's Republic)
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (hsPDA) is associated with increased comorbidities in neonates. Early evaluation of hsPDA risk is critical to implement individualized intervention to improve prognosis.
Objective: To establish early risk stratified models of hsPDA and identify the effect of genetics on model.
Design/Methods:
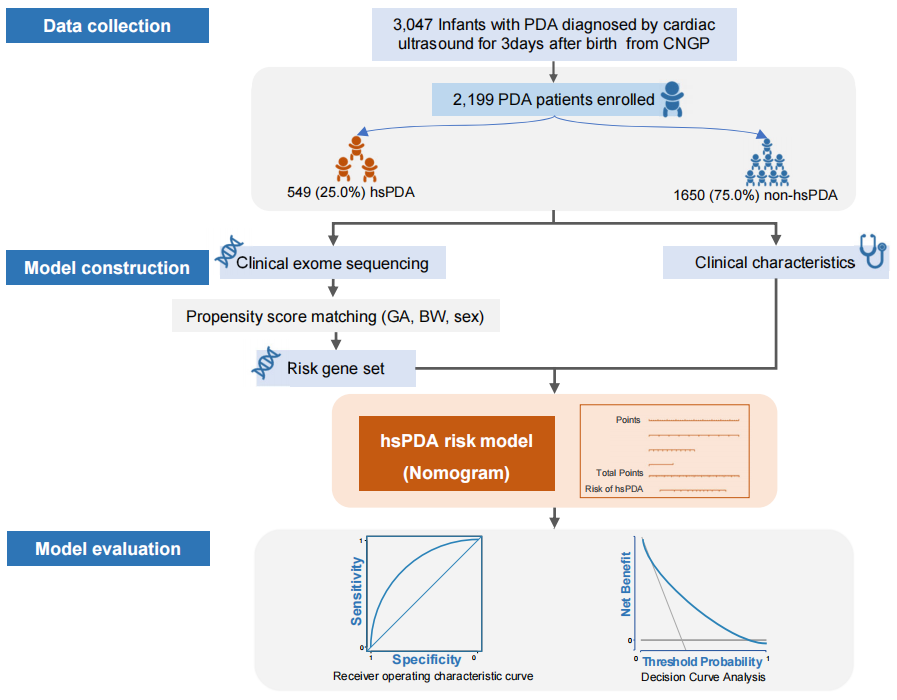
We enrolled infants who were diagnosed with PDA after three days of life and performed the exome sequencing. The collapsing analyses was used to find risk gene set (RGS) of hsPDA for model construction. The credibility of RGS was proved by RNA sequencing. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to establish models combining clinical and genetic features. The models were evaluated by area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) and the decision curve analysis (DCA).
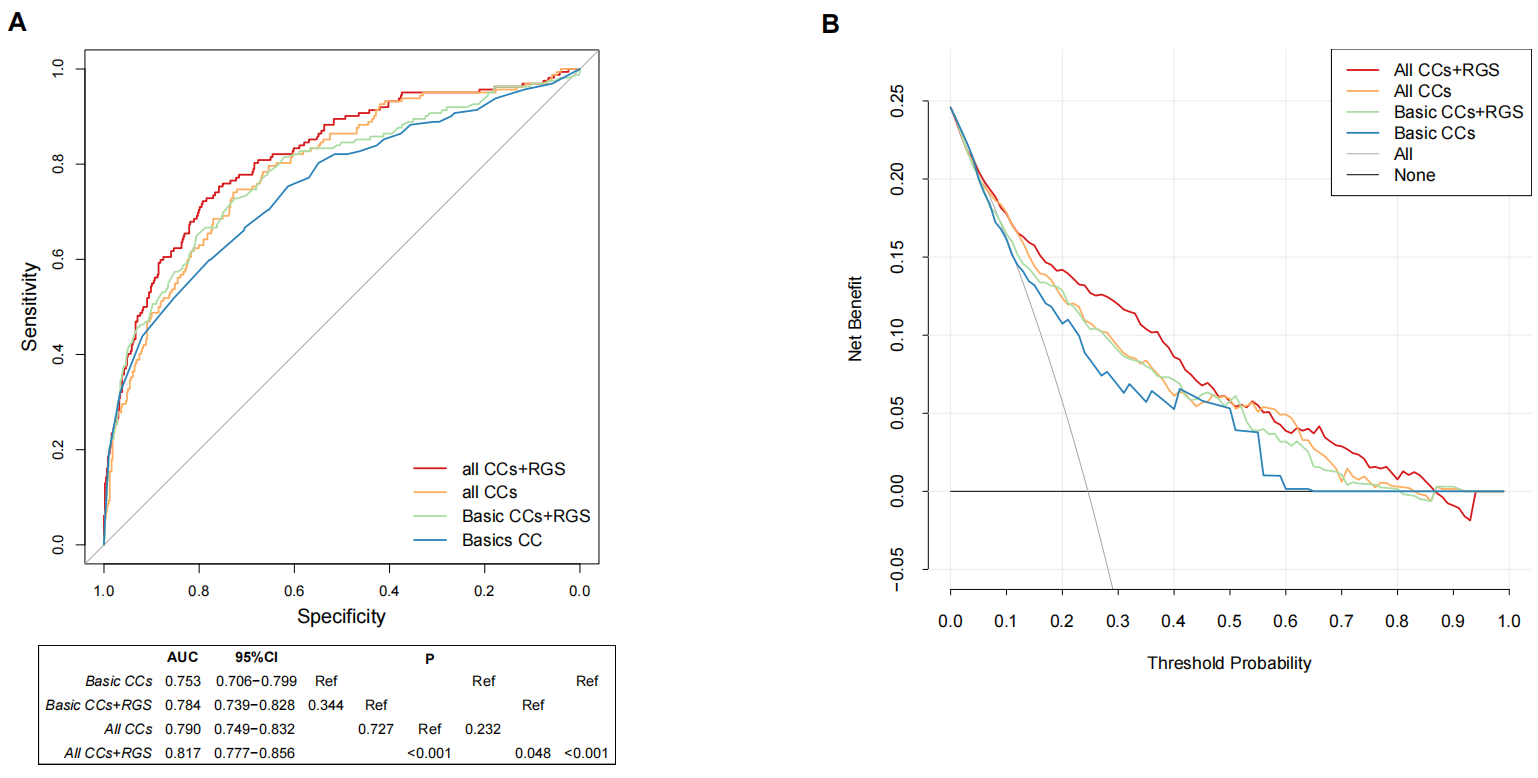
Results: In this retrospective cohort study of 2199 PDA patients, 549 (25.0%) infants were diagnosed with hsPDA. The model (All CCs) based on six clinical variables were acquired within three days of life, including gestational age (GA), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), the lowest platelet count, invasive mechanical ventilation, positive inotropic drugs and vasoactive drugs. It has an AUC of 0.790 (95%CI 0.749-0.842), while the simplified model (Basic CCs) including GA and RDS has an AUC of 0.753 (95%CI 0.706-0.799). There was a certain consistency between RGS and differentially expressed genes of DA in mice. The AUC of the models was improved by adding RGS, and the improvement was statistically significant (All CCs vs. All CCs+RGS: 0.790 vs. 0.817, P< 0.001). The DCA demonstrated that all models were clinically useful.
Conclusion(s): The models based on clinical and genetic factors can accurately stratify the risk of hsPDA in three days after birth, and the genetic factors contributed to improving the model performance.