Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 4
113 - Prediction of pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants using miRNAs in early tracheal aspirate samples
Publication Number: 113.426

Roopa Siddaiah, MD FAAP (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Penn State Health Children's Hospital
Hershey, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Pulmonary hypertension (BPD-PH) associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a severe complication of preterm birth associated with high mortality. However, because the clinical signs and symptoms of BPD-PH overlap with that of BPD, a high level of suspicion needs to be employed to perform tests to diagnose BPD-PH. Hence, the current clinical practice is to screen for BPD-PH via echocardiogram at 36 weeks in preterm infants with BPD. Identifying at-risk preterm infants will help early diagnosis. We have previously identified a panel of 20 miRNAs in tracheal aspirate (TA) differentially expressed in BPD-PH.
Objective:
To analyze the predictive value of target specific miRNA panel in early TA samples in extreme preterm infants
Design/Methods:
We collected TA samples from 22 preterm infants born < 28 weeks of gestation within first 7 days of age. The samples were frozen at -80 C until analysis. The samples were them thawed, RNA extracted using Norgen miRNA purification kit and miRNA was analyzed using small RNA-sequencing libraries were prepared from 5-25 ng total RNA. The resulting high throughout sequencing data using QIAseq miRNA Library kit (QIAGEN). Of the original 20 miRNAs, only 16 were expressed in the 7 day old samples in our new cohort. Logistic regression was calculated for the 16miRNAs (hsa-miR-29a-3p, hsa-miR-542-3p, has-miR-624-5p, hsa-miR-183-5p, hsa-miR-3131, hsa-miR-501-3p, hsa-miR-101-3p, has-miR-101-5p, hsa-miR-3128, hsa-miR-128-3p, hsa-miR-628-3p, hsa-miR-24-3p, hsa-miR-1255b-5p, hsa-miR-205-5p, hsa-let-7i-3p and has-let-7i-5p) to calculate RUC area under the curve.
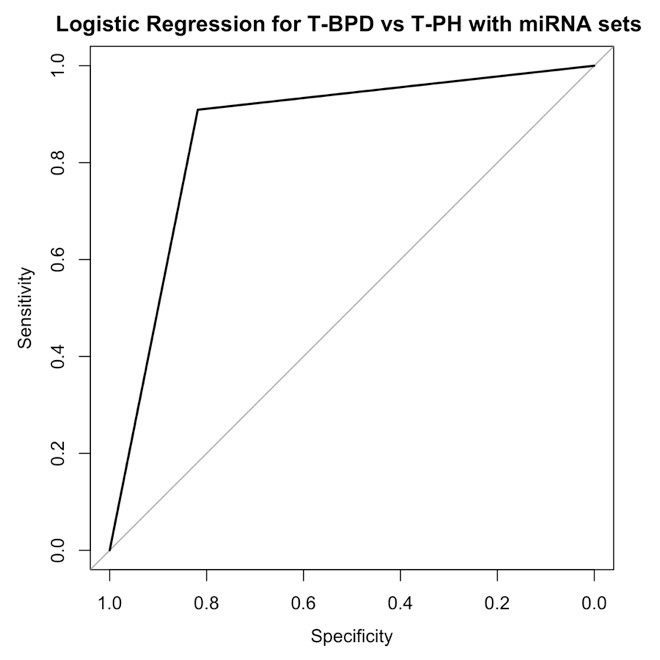
Results: Of the 22 infants, 11 of them were diagnosed with BPD-PH at 36-40 weeks of gestation based on their echocardiogram findings and 11 of them with Grade 2-3 BPD (2019 NICHD/NRN classification). Logistic regression calculation (Table 1) of the 16 miRNAs comparing infants who went on to develop BPD-PH vs BPD at 36 weeks of PMA revealed area under the ROC = 0.86 with sensitivity and specificity of 83% and 82% respectively (Figure 1) of predicting BPD-PH in those with high risk of developing BPD.
Conclusion(s): A panel of 16 miRNAs expressed in early TA samples have significant predictive value in identifying extreme preterm infants that are at high risk for developing BPD-PH at 36 weeks PMA. This panel once validated in a larger cohort has the potential as a clinical tool to closely monitor high risk infants for pulmonary vascular disease and intervene as needed with target oxygen saturations, optimize nutrition and fluid goals and early echocardiogram to screen for BPD-PH